Overview

Sparkflows enables Complex Big Data Engineering with ease. It has 200+ building blocks and a smart workflow editor for building out the workflows.
Sparkflows also enables interactive execution of the nodes of the workflow making it easy to view the output of any given step.
Sparkflows has a variety of Processors for enabling Big Data Engineering:
-
Connectors for reading from various Big Data Stores
-
Data Validation
-
Data Cleaning & Transforms
-
De-duplication of data
-
Storing data into various Big Data Stores
Information Technology

Connect various SQL for powerful transforms
SQL is extremely powerful and most widely used. Sparkflows takes it to a totally another level but enabling reading data from various Data Sources and then adding any number of SQL statements to process the data.
The output of one SQL is fed as input to another SQL. This enables doing complex transforms, yet keeping the individual SQL simple enough.
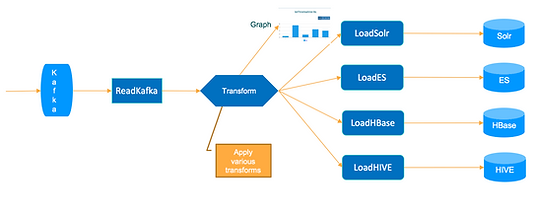
Seamlessly Perform Stream Processing
Sparkflows enables powerful, complex stream processing with ease.
Read from Apache Kafka, perform complex transforms, save results to Apache HBase, Apache Kafka, etc.
Along the way, also perform complex analytics. All of these are achieved in minutes including running on Big Data and on the Cluster.
Perform Complex Dedup with Ease

Perform complex dedup with ease with Sparkflows.
Big Data and Data Lakes is a place where many different datasets come together. In many instances there is no specific common ID connecting 2 datasets. In these cases, the ability to match the records across them bring great value to the Business and variety of Use Cases.
With Sparkflows perform complex dedup with fuzzy matching between datasets. Fine tune your algorithms selection, weights for the various columns with easy to get amazing results in a matter of 1-2 hours.

Dashboards
Sparkflows also enables building rich dashboards in minutes. Dashboard editor allows dragging and dropping nodes from any of the workflows into a canvas.
When the workflows execute, the dashboard is populated with the output of the specified nodes.